RPI Reports: Declining Well Production Will Boost the Workover and Coiled Tubing Market
Over the last few years, the well workover market has been growing steadily, despite periodic crises in the oilfield service market and oil and gas industry. There was a strong reason for this – deterioration of the well stock forced the market to increase the number of workover operations. This factor remained relevant in 2018 and it will still be important in the mid-term. In addition to the increase in the number of workover operations, we should expect technological improvements, in particular, an increase in the number of coiled tubing workover operations. The future of these two interconnected markets – workover and coiled tubing – should be viewed with cautious optimism.
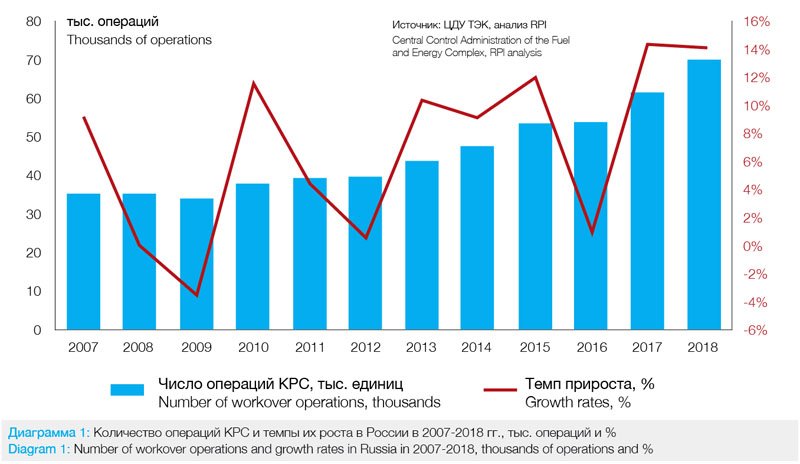
The number of workover operations in Russia has been increasing steadily since 2009. In total, over this period it increased by 107.1% from 33,900 operations in 2009 up to 70,000 operations in 2018. The annual growth rate of the number of workover operations over this period also increased (from -3.7% in 2009 to 14.4% in 2017), with an average annual growth rate of 8.5% (Diagram 1).
The number of workover operations in all oil-producing regions continued to grow during this period. However, only two regions were the main drivers of this growth: Western Siberia and Volga-Ural region. Of the total increase in the number of workover operations in 2009-2018 (+36.2 thousand operations), 25.1 thousand operations were performed in Western Siberia and 6.3 thousand operations – in Volga-Ural region (see Diagram 2).
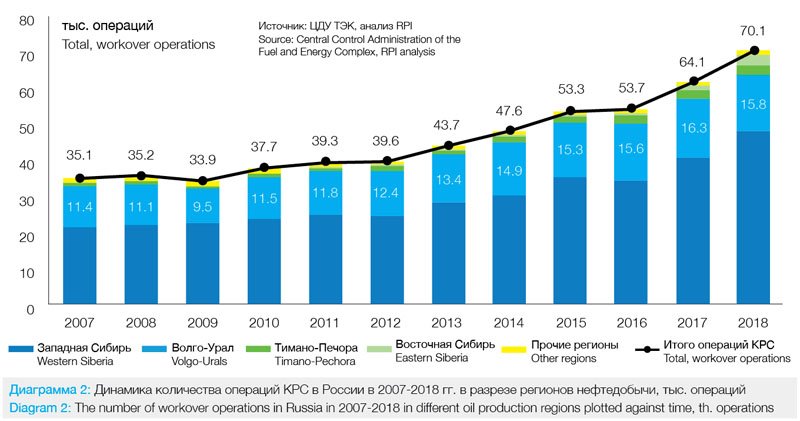
operations in 2018 increased by 14.1%. That resulted in an increase of the number of workover operations by 8.7 thousand as compared to 2017, and the total number reached approximately 70.1 thousand workover operations.
As mentioned above, Western Siberia played a key role in the workover market growth in 2018, providing 80% of the total growth. It was provided primarily by Rosneft subsidiaries: RN-Yuganskneftegaz (+8060 operations, +126% as compared to 2017), Sakhalinmorneftegaz (+1647 operations, +706%) and RN-Purneftegaz (+907 operations, +48%).
In 2018, Western Siberia and the Volga-Ural regions had a share of 90% of the total workover market with 68% and 22% shares respectively. The high market share of these two regions in comparison to the total volume of workover operations is primarily due to a significant proportion in the total well stock: 94% of all oil production wells in Russia are located in Western Siberia and Volga-Ural regions.
The number of workover operations per well was the highest in Eastern Siberia and Timan-Pechora regions in 2018 with 0.89 and 0.66 operations per well, respectively, and the lowest in Volga-Ural region with 0.28 operations per well.
In monetary terms, the workover market in 2009-2018 demonstrated steady growth, increasing by 181% over this period with an average annual growth rate of about 12%. As a result, in 2018 the workover market reached the level of 161 billion rubles. Last year the workover market grew by 22.8 billion rubles, demonstrating an annual growth rate of 16.4% (Diagram 3).
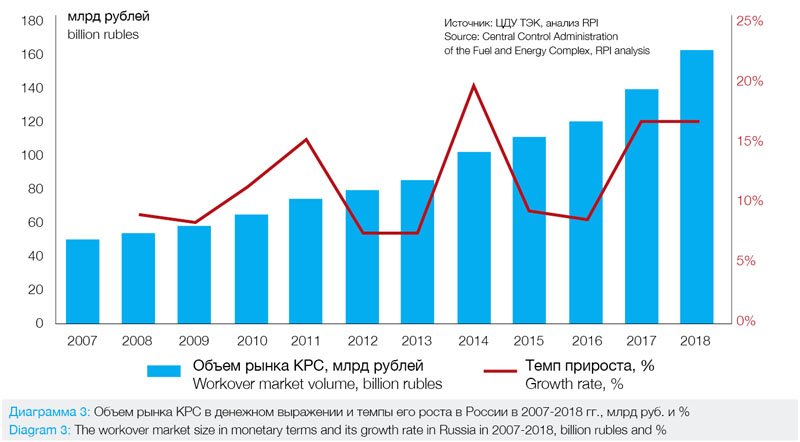
The average cost of one workover operation in 2018 in Russia increased by 2% and reached 2.3 million rubles for a single operation.
As in 2017, the growth of the Russian workover market in 2018 accounted for 22.8 billion rubles, which was primarily due to an increase in the number of workover operations (+20.0 billion rubles) and, to a lesser extent, due to an increase in the cost of one operation (+2.8 billion rubles).
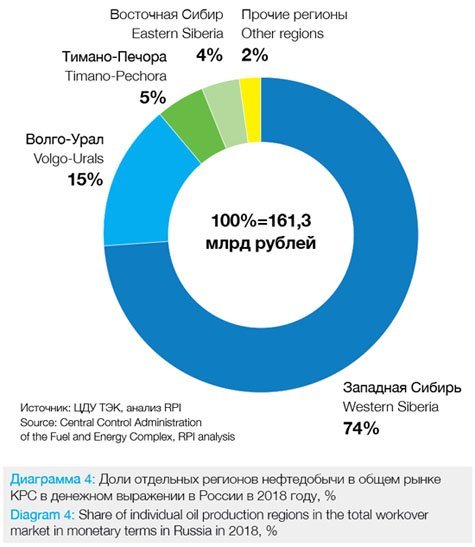
In 2018, Western Siberia and the Volga-Ural region in total accounted for 88% of the market in money terms with 74% and 14% market shares, respectively (Diagram 4).
In 2018, Western and Eastern Siberia were the regions where Russian workover market grew by 17.3 billion rubles and 3.6 billion rubles, respectively. Other regions (including Caspian, North Caucasian, Okhotomorskaya and other petroleum provinces) made the least contribution to the growth of the workover market, reducing the volume of operations by 0.2 billion rubles.
The growth of regional sectors of Russian workover market was mainly driven by one parameter – an increase in the number of operations, except for the Volga-Urals where the market growth was due to an increase in the cost of workover operations.
Last year the cost of workover operations reached 3.14 million rubles per operation in Timano-Pechora, 2.52 million rubles in Western Siberia, 2.37 million rubles in Eastern Siberia, 1.48 million rubles in the Volga-Ural region and 2.26 million rubles in other regions. The change in the average cost of a workover operation was different in each region: from a 27.9% decline in Eastern Siberia to a 9.2% increase in the Volga-Ural region.
In the Volga-Ural region, the increase in the average cost of a workover operation was mainly due to an increase in the cost of operations at Orenburgneft, Samaraneftegaz and Belkamneft. Orenburgneft’s share in Volga-Ural market in 2018 was 10% in physical terms and 15% in monetary terms, and the growth in the cost of workover operation in this company was 48.5%. Thus, Orenburgneft made a key contribution to the growth of the average cost of workover operations in the Volga-Ural region.
In Eastern Siberia, the decline in the cost of workover operation at Sakhalinmorneftegaz, which operates the Odoptu-more (North Dome) offshore oil and gas field, had a significant impact on the average workover cost in the region. As one of the most relevant companies in the region (39% of the regional market in physical terms and 65% in monetary terms), the company reduced the average cost per operation by 33%, which impacted the total region performance.
Customers and Contractors
Last year, Rosneft, Surgutneftegas and LUKOIL provided 75% of the total workover market in physical terms with shares 51%, 12% and 12%, respectively.
Calculations of the ratio of the number of workover operations to the number of production wells showed that the maximum ratio in 2018 was 0.83 for Rosneft, 0.50 for Gazprom Neft and 0.46 for Slavneft while the minimum ratio was demonstrated by Tatneft and other companies with ratios 0.15 and 0.27 respectively. Differences between companies are primarily associated with the field depletion coefficient.
In monetary terms, in 2018 the workover market grew by 22.8 billion rubles. Rosneft (+18.7 billion rubles), Surgutneftegaz (+5.1 billion rubles) and LUKOIL (+3.2 billion rubles) made the largest contribution to the market growth.
Changes in the cost and volumes of workover operation had a different impact on changes in the workover market volume for different customers. For example, the growth of Surgutneftegaz and LUKOIL was driven by an increase in the cost of operations, and that of Rosneft – by an increase in the number of operations.
In monetary terms customer market profile is similar. In total, Rosneft, Surgutneftegas and LUKOIL provided 84% of the workover market with shares 37%, 33% and 14% respectively.
In general, it was observed that the process of market concentration is still in progress: as compared to 2017, the top three customers increased their total share in 2018 from 70% to 75% in physical terms, and from 78% to 84% in monetary terms.
One of the specific features of the Russian workover market is the presence of a significant number of small companies with few workover teams. These companies work under subcontracts with larger service companies, often at dumping rates, and are therefore at risk of bankruptcy and liquidation. Regular rotation of companies is one of the features of this market sector. Re-registration of liquidated companies is a common practice.
In the Russian market, small independent companies perform approximately 24% of all workover operations annually in physical terms (in 2018, the share of other companies decreased due to, among other things, a larger number of market players as compared to previous periods). The decrease in the share of small companies by 1-3% annually is largely due to the centralization of the oilfield services market and the consolidation of service companies’ subdivisions within vertically integrated oil companies. More than two thirds of workover operations in Russia are performed by large, financially stable companies.
In 2018, RN-Servis’s share of the workover market increased from 23% to 28% due to an increase in the number of workover operations in Western Siberia. The volume of workover operations performed by this company increased by 38% up to 19.6 thousand operations. Surgutneftegas increased the volume of operations but this increase was at a rate lower than the average market rate, which resulted in the decrease in its share from 15% to 13%.
In general, in 2018 most of major contractors experienced an increase in the number of operations.
In 2018, the market continued the trend of strengthening of the service companies positions within vertically integrated oil companies. This is primarily due to the fact that the share of leading oil and gas customers has increased. When service contractors are the part of the company, most of the work is to be transferred to its subsidiaries in case it is technically feasible to do so. However, this does not change the fact that independent companies are still involved.
The comparison of the data on workover market development in terms of customers and contractors indicates that, for example, the share of Rosneft as a customer increased by 8% as compared to 2017, while the share of RN-Servis as a contractor increased by only 5%. This fact demonstrates a common practice of involving third-party independent companies for performing workover operations. Surgutneftegas performs almost all operations through its own divisions. Other operators (LUKOIL, Gazprom Neft, etc.) are more open to third-party contractors.
What is the State of Coiled Tubing Market?
Evaluation of the actual volume of the coiled tubing market was carried out based on the following indicators:
• the number of hydraulic fracturing and multistage fracturing operations in new and existing wells;
• number of workover operations by the type;
• expert estimates of the development of coiled tubing application in fracturing operations by oil and gas regions;
• expert estimates of CT utilization by CT operation type and by oil and gas region;
• rate of horizontal wells commissioning and increase in the share of horizontal wells in the total well stock;
• actual and estimated cost of coiled tubing operations for hydraulic fracturing, workover purposes, drilling and
sidetracking.
As a result of RPI research, it was found that the coiled tubing market is one of the most dynamic segments of the oilfield services market. This fact is evidenced by the increase in the number of coiled tubing units over the last 11 years by approximately three times, accompanied by a 2.5-fold increase in the number of operations.
At present, the use of coiled tubing in the Russian market is primarily focused on the following operations:
• fracturing and multistage fracturing in new wells;
• workover operations including bottom-hole treatment;
• preparation of wells for hydraulic fracturing and sidetracking;
• well stimulation after hydraulic fracturing and sidetracking;
• commissioning and workover operations in injection wells (stimulation of new wells);
• other workover operations.
The use of coiled tubing in other segments (drilling and sidetracking) is rather limited (except for Surgutneftegas), which is particularly noticeable in comparison with international experience, especially in the USA and Canada.
The coiled tubing market in Russia began to develop in 1998. However, rapid quantitative and qualitative growth was indicated only in 2007-2018, when the number of operations increased by 153.9%, from 8.6 thousand in 2007 up to 21.9 thousand in 2018 (Diagram 5).
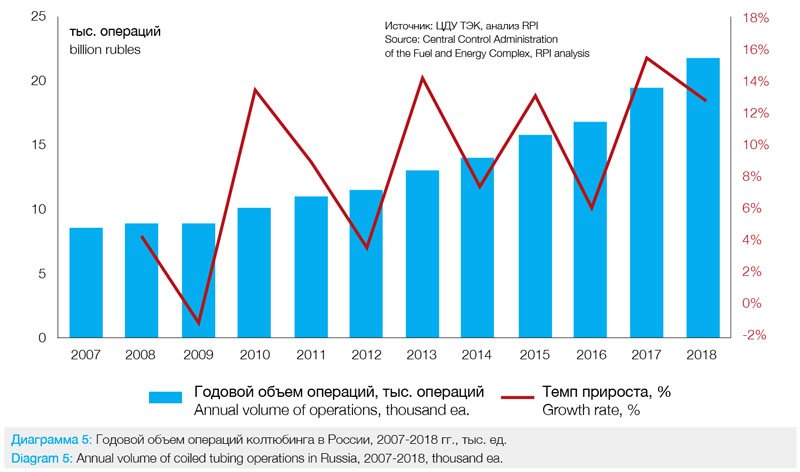
At present, the usage of coiled tubing differs significantly by oil and gas company, which is primarily due to the approach of oil and gas companies to service: some companies introduce and apply coiled tubing technologies at all stages of drilling, stimulation and workover, while others use coiled tubing only for certain service operations.
For the whole country the use of coiled tubing until 2010 was a consequence of the increase in the number of workover operations with coiled tubing, and starting in 2011, the growth of coiled tubing operations was further boosted by the expansion of oilfield services through the use of coiled tubing, in particular for multistage fracturing operations and for commissioning of horizontal wells.
The market situation last year is described as follows. In 2018, the number of coiled tubing operations increased by 2.6 thousand units (+12.8%) up to the level of 21.9 thousand operations as compared to 2017. The main growth was concentrated in bottomhole treatment, hydraulic fracturing and multistage fracturing segments and other workover operations.
The largest share in the total number of coiled tubing operations in 2018 was for bottom-hole treatment and well stimulation (excluding hydraulic fracturing) segments – 41.2%, and for fracturing and multistage fracturing segments – 26.8%.
As of 2018, the key regions of coiled tubing application were Western Siberia (78.8% of all operations in Russia) and the Volga-Ural region. This is due to the growing number of wells at the fields in late stages of development which is characterized by the increase in the volume of hydraulic fracturing, workover and sidetracking operations.
The change in the number of coiled tubing operations by oil production region in 2007-2018 was mainly caused by the increase in the number of workover and fracturing/multistage fracturing operations using coiled tubing. Drilling and sidetracking with coiled tubing are only drivers for Western and Eastern Siberia.
From 2007 to 2018, the cost of CT operations in Russia had been increasing annually, and the whole coiled tubing market had been growing in monetary terms. The average annual growth rate for this period was 22.6%. In 2018, the coiled tubing market in monetary terms amounted to 79.4 billion rubles (Diagram 6), the annual growth of the market volume in monetary terms was 20.2% as compared to 2017.
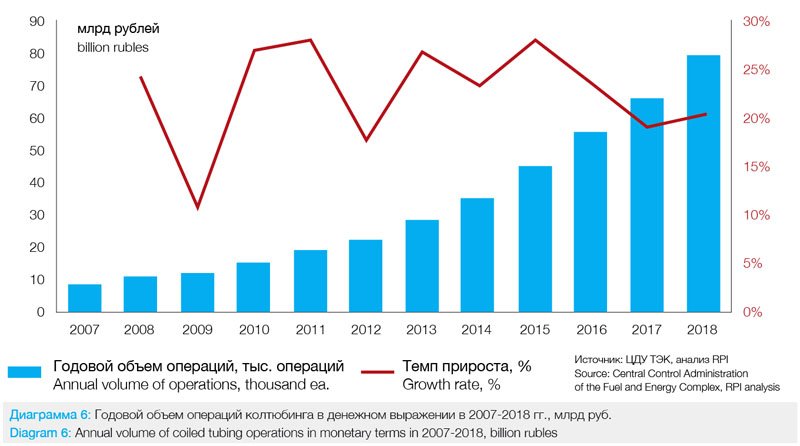
In terms of market segments, the highest growth rate over the period from 2007 to 2018 was demonstrated by fracturing and multistage fracturing segments (+46.0 billion rubles), which provided 64.9% of the coiled tubing market growth over this period.
The most expensive segment of CT operations in monetary terms is fracturing, including multistage fracturing in new wells, which amounted to 48.3 billion rubles in 2018 (60,8%). The total volume of CT workover operations was 27.9 billion rubles (35,2%). Coiled tubing operations for drilling and sidetracking accounted for 4.1% or 3.2 billion rubles.
The largest coiled tubing workover segments in monetary terms in 2018 were:
• Bottomhole treatment – 10.8 billion rubles (13.7% of the total coiled tubing market);
• preparation and stimulation after hydraulic fracturing – 9.1 billion rubles (11,4%);
• preparation and stimulation after sidetracking – 2.8 billion rubles (11,4%);
• commissioning and workover operations in injection wells (stimulation of new wells) – 3.0 billion rubles (3,7%).
It should be noted that the largest share of the coiled tubing market in physical terms was represented by workover operations – 71.2%, while in monetary terms it was only 35.2%. The opposite is true for the fracturing and multistage fracturing segments – in physical terms its share in 2018 was 26.8%, while in monetary terms this segment was the largest in terms of the number of operations – 60.8%.
The main customers of coiled tubing services in Russia are vertically integrated companies. In 2018, over 80% of coiled tubing operations were carried out for Rosneft, Surgutneftegaz, LUKOIL, Gazprom Neft and Slavneft. Deteriorating resource base is forcing the largest vertically integrated oil companies to invest more and more in production intensification and enhanced oil recovery methods, which results in the increased number of drilling, sidetracking, hydraulic fracturing and workover operations, which are the main drivers of coiled tubing operations in Russia.
As for customers, operators’ shares were distributed primarily in accordance with the work scope of horizontal drilling, as well as the number of sidetracking operations. However, technology-wise, there is a noticeable difference in the application of coiled tubing in different companies.
Rosneft has the highest demand for CT operations. Since 2015, Rosneft has been pursuing a policy of acquisition of independent oilfield service companies in order to increase its own oilfield service segment. Currently, Rosneft owns seven coiled tubing fleets as part of RN-GRP. In addition to its own fleets, Rosneft engages third-party contractors. One of the largest CT projects is the Vankor field development and new projects in Yamal.
Surgutneftegas performs 14.8% of the total number of coiled tubing operations in the country. The largest share of CT operations in Surgutneftegaz is represented by workover operations – 54.1% of all coiled tubing operations in this company, hydraulic fracturing and multistage fracturing in new wells – 24.6%. Surgutneftegas is the largest company that uses coiled tubing drilling technology.
LUKOIL performs 10.1% of the total number of coiled tubing operations in the country. The largest share of CT operations in LUKOIL is represented by workover operations – 69.4% of all coiled tubing operations in this company, hydraulic fracturing and multistage fracturing in new wells – 24.6%.
The structure of the coiled tubing contractors’ market changed in the past year. For example, due to the ongoing anti-Russian sanctions, several foreign CT service players left the Russian market and were replaced by new domestic companies, which are pursuing a policy of price dumping in a highly competitive market.
Along with new oilfield services companies, drilling companies started to purchase coiled tubing units in order to enter the coiled tubing market. This will allow these companies to occupy a promising niche of coiled tubing drilling in the future. Experts estimate that the ratio of domestic and foreign companies in the coiled tubing market is 80:20. American companies remained the largest share among the foreign players in the Russian market. However, CT service is often not a key product line in their business in Russia.
Customers’ requirements to technical equipment of coiled tubing fleets, such as length and diameter of pipes (length up to 5 thousand meters, diameter up to 1.75 inches) are becoming more demanding. For this reason contractors need to upgrade fleet equipment to improve competitiveness in the market, and also optimize the cost of coiled tubing operations so that the CT operations segment can compete in the oilfield services market with traditional workover operations. The emergence of new market players, for example, drilling companies with CT units, makes this optimization necessary in order to stay in the niche of coiled tubing contractors.
The current geopolitical and economic environment stimulates the development of domestic manufacturing of coiled tubing equipment. The imposition of sector-specific anti-Russian sanctions resulted in the policy of import substitution. For example, FrakJet-Volga launched a pipe plant that manufactures pipes with diameters ranging from 25.4 to 88.9 mm and lengths up to 9,000 mm with full compliance with the API 5ST standard in Russia.
In the mid-term, companies that develop their own manufacturing will occupy a stronger position in the coiled tubing market, as they will be able to reduce the cost of operations and compete on the price.
As a result of different tendencies, the balance of power in the market is as follows. The following companies carried out the largest number of coiled tubing operations last year:
• Surgutneftegas -13.9%;
• Packer Servis – 8.8%;
• RN-GRP – 8.6%;
• Schlumberger – 8.3%.
We believe that the future development of coiled tubing market will be supported by long-term drivers. These drivers will include:
• increase in the number of fracturing and multistage fracturing operations in new wells and subsequent coiled
tubing operations;
• increase in the number of coiled tubing workover operations, in particular: bottomhole treatment, commissioning of injection wells, preparation for hydraulic fracturing, sidetracking and stimulation after fracturing and sidetracking;
• increase in the number of sidetracking operations, primarily for drilling horizontal wellbores;
• commissioning of new wells, primarily horizontal wells.
Market Profile in Money Terms
The development of the coiled tubing market is described as follows. The main driver of the coiled tubing operations growth in monetary terms in 2007-2018 in Russia is hydraulic fracturing, primarily multistage fracturing in new wells.
Coiled tubing operations for a single stage hydraulic fracturing in 2007-2018 grew 8.5-fold from 2.3 billion rubles in 2007 up to 19.5 billion rubles in 2018. However, in 2018, the coiled tubing market for a single-stage fracturing decreased by 2.5% (from 20.0 billion rubles in 2010 to 19.5 billion rubles in 2011). This was due to the reduction in the number of single-stage fracturing operations caused by the diversification of demand for multistage fracturing operations in the oilfield services market as a whole.
Last year, coiled tubing operations for multistage fracturing dominated in the coiled tubing fracturing segment in monetary terms, accounting for 59.5%, which is equivalent to 28.7 billion rubles. As compared to 2011, when this technology was introduced to the oilfield services market, this segment grew more than 15 times.
Positive growth of the number of CT operations is also observed in the workover segment, primarily in bottomhole treatment, preparation for hydraulic fracturing and sidetracking, commissioning and workover of injection wells (stimulation of new wells) – the total share of these operations in the total coiled tubing market in monetary terms in 2018 amounted to 35.1%.
Despite the mid-term growth in demand for drilling and coiled tubing market, the total share of coiled tubing operations in the coiled tubing market will not exceed 5% in physical terms. This is due to the high cost, technical difficulties (length and diameter of coiled tubing) and labor costs.
The coiled tubing market has the greatest prospects for development in oilfield segments where stable growth is forecasted (growth of the number of fracturing and multistage fracturing operations, workover operations, horizontal wells, including lateral horizontal wellbores; sidetracking).
Forecasts
When forecasting the number of workover operations in 2019-2030 we have considered the following factors:
• forecast of oil production in Russia in 2019-2030;
• well stock production period;
• dynamics of the share of idle production wells;
• dynamics of workover complexity;
• dynamics of changes in the structure of operations by the type of repairs;
• possible impact of sanctions restrictions on the workover market.
The need to maintain the oil production level in 2019-2030 will force companies to use workover teams to keep wells in good working condition. There will be two more factors to stimulate the demand for workover operations during this period: well stock growth and deterioration, especially in conventional production regions. All of this will affect the frequency of application of enhanced oil recovery methods.
As a result, in 2019-2030 the annual number of workover operations will continue to grow. In 2030, this value will reach the level of 116.9 thousand operations, which is 67% more than that in 2018. Decrease in the growth rate of the number of workover operations is due to the decrease in the number of drilling operations, as well as sidetracking and hydraulic fracturing.
By 2025, it is expected that many large mature deposits will be depleted, and operators will concentrate on smaller deposits, which will affect the growth rate of the workover market.
The number of workover operations will grow faster than the number of wells. The number of producing wells will increase by 20% to 184,000 wells along with a 67% increase in the number of workover operations in 2018-2030. Thus, the number of workover operations per oil producing well will increase from 0.46 in 2018 to 0.64 in 2030.
Regionally, Western Siberia (66.4% of the country’s total number of operations) and the Volga-Ural region (19.3%) will continue to account for the largest number of workover operations in 2030.
Increase in the number of workover operations by 46.8 thousand in 2018-2030 will be primarily supported by a quantitative growth in Western Siberia (+30 thousand operations), the Volga-Ural region (+6.8 thousand) and Eastern Siberia (+5.8 thousand).
In 2030, Western Siberia and the Volga-Ural region will account for 85% in the overall structure of the workover market, with its share in the Russian oil well stock at the level of 92% (62% and 30%, respectively).
The number of workover operations per production well will still be the highest in Eastern Siberia – 1.37 per well, and the lowest in the Volga-Ural region – 0.41 per well. This differentiation is due to the different age of the producing fields. In Eastern Siberia workover operations are carried out for changing the type of existing wells and stimulation of new wells. In the Volga-Ural region the oldest wells are liquidated.
In monetary terms, by 2030, the workover market will grow by 171% up to 436.6 billion rubles. The forecast of workover market volume takes into account inflation in 2019-2030, which, according to the forecasts from the Ministry of Economic Development, will be within 4% per year. In this regard, the growth of the workover market in 2019-2030 in the amount of 275.3 billion rubles will primarily be due to the increase in the number of operations (by 174.7 billion rubles). The increase in the cost of workover makes a slightly less significant contribution to the growth of the workover market – by 100.5 billion rubles.
In regional terms, all regional segments of the market will continue to grow, while the dominating positions of West Siberia (72%) and Volga-Ural region (12%) segments will remain unchanged. In 2019-2030, Western Siberia will make the greatest contribution to the growth of the Russian workover market, increasing the volume of this regional segment by 193.7 billion rubles. The growth of regional segments of the Russian workover market will occur mainly due to the increase in the number of operations, rather than due to the increase in the cost of services.
In regional terms, in 2030, the cost of workover operation will reach 3.75 million rubles on average in Russia. The average increase in the cost of workover operations in 2018-2030 will be 62.3%.
The development of the coiled tubing market is presented as follows. The following factors and indicators were taken into account when making the forecast of coiled tubing market forecast:
• fracturing and multistage fracturing market forecast in regional terms;
• workover market forecast by workover type in regional terms;
• drilling market forecast;
• sidetracking market forecast;
• expert estimates of CT utilization in fracturing/multistage fracturing operations;
• expert estimates of CT utilization by CT operation type and by oil and gas region;
• dynamics of total and specific effects of fracturing and sidetracking;
• forecast dynamics of the specific share of horizontal drilling in the total drilling volume;
• evaluation of production rates of horizontal wells;
• evaluation of the length of horizontal sections;
• the impact of sanctions on equipment availability in service companies and the financial status of coiled tubing customers;
• estimated cost of coiled tubing operations in various oilfield service segments;
• official government forecasts of social and economic development of Russia in the mid-term;
• forecasts from industry experts regarding technological development of the coiled tubing market.
RPI’s research has shown that in the mid-term the demand for coiled tubing services in Russia will continue to grow due to the increasing rate of commissioning of horizontal wells and the increasing use of fracturing, multistage fracturing and workover operations. A stable demand for coiled tubing operations will be supported by the obvious advantages:
• reduced workover time due to the fact that coiled tubing operation is performed without killing the well;
• reduced negative impact on the reservoir;
• improved well control;
• ability for underbalanced drilling.
As a result, by 2030, the number of coiled tubing operations will increase by 166% to 58.2 thousand operations.
The increase in the number of operations up to 2025 at an average annual rate of 7.6% will be due to the commissioning of large fields in the Bolshekhetskaya basin, Evenkiya region and in the south of the Yamal Peninsula. Over the period from 2025 to 2030, the number of coiled tubing operations will increase by 10.1% annually. This is due to deterioration of the production well stock, where more workovers and other methods of enhanced oil recovery using coiled tubing will be carried out to increase and maintain production rates. There will be an increase in the number of sidetracking operations. As for stimulation of new vertical and directional wells, there will be less demand for coiled tubing operations due to a higher demand for horizontal drilling as compared to vertical drilling.
In the mid-term, there will be significant changes in the coiled tubing market structure. High-cost market growth is expected due to the growth of the number of CT drilling operations (sidetracking and pay zone penetration), multistage fracturing, etc. Increase in horizontal drilling volume will lead to an increase in the number of well stimulation and coiled tubing logging operations. This will also lead to the application of new CT-conveyed EOR technologies.
In 2019-2030, the largest growth of coiled tubing operations will be observed in Western Siberia and the Volga-Ural region, primarily for well stimulation after fracturing, multistage fracturing, bottomhole treatment, drilling of horizontal wells and sidetracking. CT operations during drilling will be most in-demand in Eastern Siberia.
The coiled tubing market has significant potential for growth by 2030: by 248% in money terms. The average annual growth rate in money terms will be 11.0%. This is due to the increase in the number and cost of certain operations caused by the increase in technological complexity.
We expect that the emergence of coiled tubing manufacturing in Russia will prevent the cost of coiled tubing operations (primarily coiled tubing workover) from rising, which will make coiled tubing workover operations more competitive than conventional coiled tubing operations.
The most expensive operations will be fracturing and multistage fracturing using coiled tubing. In some cases, the cost of coiled tubing service will exceed 20 million rubles per operation. Coiled tubing drilling and sidetracking operations in total will account for 11.2% of the coiled tubing market by 2030 due to the small number of these operations and high costs.
However, there is another driver that can further stimulate the market. This is the presence of more than 20,000 of temporarily abandoned wells that require workover. However, commissioning of these wells is possible only in case of changes in the tax system that will make it profitable. The advantage of using CT in the above-mentioned case is the ability to penetrate reservoir by underbalanced drilling using a preventor, which will have a positive effect on the efficiency of operations.
Changes in the tax system until 2030 will give the coiled tubing market an additional growth potential, both in physical and monetary terms, in the range of 5-9% of its total volume in physical terms, which can be implemented by commissioning of temporarily abandoned wells.
In this case, this segment will become a large promising niche for coiled tubing. However, since there is a great deal of dependence on government policy and a large set of uncertainties, this scenario is considered as an addition to the market forecast.
Analytical reports «Russian Well Workover Market» and «Russian Coiled Tubing Market» are issued by RPI. If you have questions related to the article and the report, please contact us by phone: +7(495) 5025433, +7 (495)7789332, e-mail: research@rpi-research.com
www.rpi-consult.ru
Vadim Kravets, lead analyst of RPI Research&Consulting






